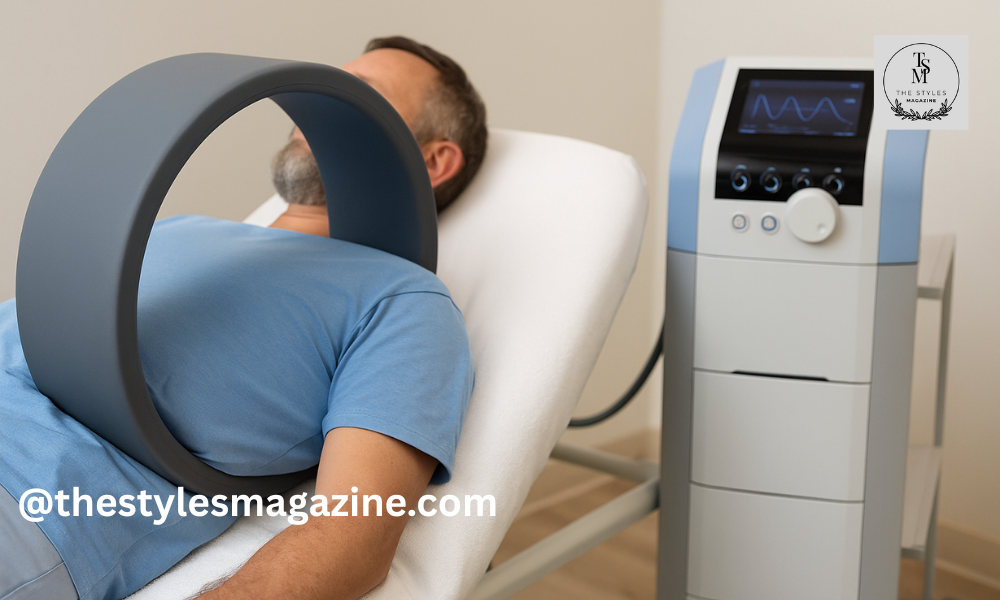
Pulsierende Signaltherapie, also known as PST, is a gentle medical treatment that uses pulsed signals to support the body’s natural healing ability. It was developed as an option for people who deal with joint pain, arthritis, bone injuries, or slow healing problems. Unlike surgery or strong medicine, this therapy works from outside the body and does not require injections or drugs.
Many people are interested in pulsierende signaltherapie because it is non-invasive, safe, and usually pain-free. The therapy aims to reduce pain, improve mobility, and encourage damaged tissue to repair itself. Some patients look to it as an alternative when other treatments have not brought enough relief. Others choose it because they want a method that feels more natural and gentle on the body.
In this article, we will explain how pulsierende signaltherapie works, what conditions it may help with, what research says about it, and what patients can expect. The goal is to give you clear, helpful, and trustworthy information so you can understand whether this therapy might be a suitable option.
How This Therapy Started And Developed
Pulsierende Signaltherapie was first introduced in the early 1990s. The idea came from Dr. Richard Markoll, who wanted to create a gentle method that could help people with joint problems and pain. At that time, many patients were struggling with arthritis and other conditions that made movement difficult, and standard treatments often came with side effects or limited success.
This new therapy was designed as a biophysical treatment, meaning it worked by using signals to support the body’s own repair process. The signals are delivered through a special device that creates a controlled electromagnetic field. This method was very different from traditional magnetic therapy. Normal magnetic therapy uses a constant field, while pulsierende signaltherapie sends carefully timed pulses. These pulses are meant to copy the natural signals that healthy joints and bones produce during movement.
Because of this difference, PST quickly gained attention in Europe and later in other parts of the world. Clinics began to offer it as an option for patients who wanted something non-invasive and drug-free. Over time, it became known not only for joint care but also for supporting bone healing and sports injuries.
How Pulsating Signals Work In The Body
Pulsierende Signaltherapie works by sending gentle electrical pulses through a magnetic field. The treatment device creates these pulses in a very controlled way, so they can reach the affected joint or bone without pain or discomfort. Patients usually sit or lie down while the device works around the problem area.
The idea is that these signals copy the body’s own natural healing impulses. In a healthy joint, tiny electrical signals are created whenever we move. These signals tell cells to build and repair cartilage, keep bones strong, and protect soft tissues. When the joint is damaged or worn down, these natural signals can become weaker.
By imitating those signals, pulsierende signaltherapie aims to remind the body how to repair itself. The therapy focuses on supporting cartilage, bone, and tissue repair. For many patients, the goal is less pain, better movement, and stronger healing in areas that have been injured or affected by disease.
Main Uses And Where It Can Help
Pulsierende Signaltherapie is most often used for joint problems. Many patients try it for arthritis and osteoarthritis, conditions where the cartilage inside the joints wears down and causes pain. By supporting cartilage repair, this therapy may help reduce stiffness and make movement easier.
Doctors also use it for bone fractures, especially when healing is slow. Some patients with delayed healing or so-called non-healing bones have reported good results after treatment. The therapy is thought to give the body an extra push to restart the natural repair process.
Tendon injuries are another common reason for using pulsierende signaltherapie. Athletes and active people sometimes choose it for sports injuries that affect movement or take a long time to heal. It is also used for back pain, where wear and tear in the spine or surrounding tissues can cause ongoing discomfort.
Some clinics mention possible benefits for osteoporosis and other long-term bone or joint issues. While more research is needed, many patients see it as a gentle option that can work alongside other treatments to improve their quality of life.
Treatment Plan: How Long It Takes And What Devices Are Used
A typical course of pulsierende signaltherapie includes 9 to 12 sessions. Each session lasts about one hour. Most clinics recommend doing the sessions on consecutive days so the body can respond to the repeated signals in a steady way. Some patients may repeat the cycle later if their condition is more serious or if they want to maintain results.
The therapy is done with special devices designed for different parts of the body. The most common is a treatment bed, where the patient lies down and the device works over larger joints like the hip or spine. There are also knee or arm devices that target single joints. For smaller areas, portable devices can be used. These allow the therapist to focus directly on the problem spot, such as the wrist, ankle, or shoulder.
The treatment does not require needles, medication, or surgery. Patients usually relax during the session, and many describe the process as simple and comfortable.
Safety, Risks, And Who Should Avoid It
Pulsierende signaltherapie is considered safe for most people. The treatment is non-invasive, meaning nothing enters the body, and it is pain-free. Patients usually lie or sit comfortably while the device delivers the signals, and many describe the experience as relaxing.
Even though the therapy is gentle, it is not suitable for everyone. People with pacemakers should avoid it, because the signals may interfere with the device. Pregnant women are also advised not to use it, as there is not enough research on safety during pregnancy. Cancer patients, especially those with tumors near the treatment area, are usually not recommended for this therapy either.
So far, very few side effects have been reported. Some patients may feel mild warmth or tingling in the treated area, but this is rare. Still, more long-term studies are needed to fully understand all possible risks. Because of this, patients should always speak with a doctor before starting pulsierende signaltherapie to make sure it is a safe choice for their condition.
What Research And Studies Say About It
Research on pulsierende signaltherapie has shown mixed results. Some studies report that patients experience less pain and better mobility after treatment. In cases of arthritis or slow-healing bone injuries, many people said they could move more easily and felt more comfortable in daily life.
However, the evidence is still limited. Not all studies are high quality, and some trials included only small groups of patients. This makes it harder to know how well the therapy works for everyone. While many clinics and patients believe in its benefits, scientists agree that more strong and long-term research is needed.
Another important point is cost. Because the scientific proof is not yet clear, many health insurance providers do not cover pulsierende signaltherapie. This means that patients often have to pay for the sessions themselves, which can be a challenge for some.
Real Patient Experiences And Clinic Use
Many patients who try pulsierende signaltherapie say they feel less pain after completing the treatment sessions. Some also notice that they can move more freely, with less stiffness in their joints. For people with long-term conditions like arthritis, even small improvements in comfort and mobility can make a big difference in daily life.
Clinics that offer the therapy describe it as safe and simple to use. Patients usually remain relaxed during the session, and most finish without any side effects. Doctors and therapists often recommend it to people who want a non-invasive, drug-free option to support healing.
Still, most experts agree that pulsierende signaltherapie works best as part of a wider treatment plan. It is not a stand-alone cure for arthritis, fractures, or other serious conditions. Instead, it can be used alongside exercise, physical therapy, or medical care to improve results. This combination approach often gives patients the best chance of long-lasting relief.
Conclusion
Pulsierende signaltherapie is a promising therapy, but it is not fully proven yet. Many patients report less pain and better movement, and clinics value it as a safe, gentle method. At the same time, science has not confirmed all of its long-term benefits, and more strong studies are still needed.
For patients who want an alternative to drugs or surgery, pulsierende signaltherapie can be a helpful option. It is non-invasive, pain-free, and usually well tolerated. When combined with other treatments, it may support healing and improve quality of life.
Looking ahead, the future of this therapy depends on continued research. If larger studies confirm its effects, it could become a more widely accepted choice in modern medicine. Until then, patients should see it as an additional tool, not a guaranteed cure.
FAQs
What Is Pulsierende Signaltherapie Used For?
It is mainly used for joint problems like arthritis, bone fractures that heal slowly, and tendon or sports injuries.
Is Pulsierende Signaltherapie Painful?
No, the treatment is non-invasive and pain-free. Most patients relax during the sessions.
How Many Sessions Are Usually Needed?
A typical plan includes 9 to 12 sessions, each lasting about one hour.
Who Should Avoid Pulsierende Signaltherapie?
People with pacemakers, pregnant women, and cancer patients are usually advised not to use it.
Does Health Insurance Cover Pulsierende Signaltherapie?
In most cases, health insurance does not cover the cost because scientific proof is still limited. Patients often pay for the treatment themselves.
Thank you for exploring our Blog! For additional captivating content, feel free to explore the corresponding category.
Disclaimer: This article about pulsierende signal therapie is for information only. It does not replace medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always speak with a qualified doctor or healthcare provider before starting any new therapy.
Shaping The Future Of Healthcare: How Clinical Trials Drive Medical Innovations