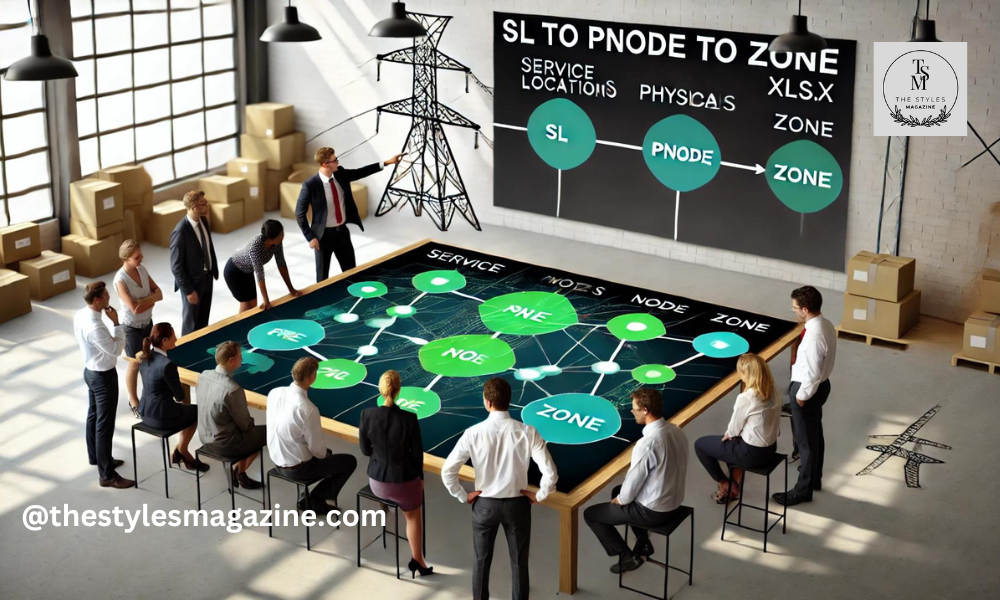
Introduction To Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping.xlsx.
SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. is a specialized Excel file used in industries like energy management, telecommunications, and network administration. This tool is designed to organize and manage the flow of data and resources efficiently across large networks or grids.
The primary function of this Excel sheet is to map Service Locations (SL), which represent areas or nodes where services are delivered, to PNodes (Power Nodes or Physical Nodes), which are essential components in distributing power or data. Once this mapping is complete, zones are allocated to group related PNodes and SLs together for easier monitoring and management.
For example, in the energy industry, SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. is used to track the distribution of electricity from power nodes to residential or commercial service locations. This allows energy managers to ensure that electricity is balanced, and outages are quickly identified. Similarly, in telecommunications, companies use this mapping to keep track of data transmission between network nodes and end-user locations.
This tool is vital for improving operational efficiency, making troubleshooting easier, and ensuring that resources are allocated where they are needed most. The Excel format also makes it accessible and easy to use, even for those without advanced technical training. Its structured format allows users to input data systematically, ensuring that information about nodes and zones is organized and easy to access whenever needed.
Key Components Of Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping
Service Locations (SLs):
Service Locations, or SLs, are the specific geographical points where services are delivered. In industries like energy management, these could be homes, businesses, or industrial sites receiving electricity. In telecommunications, SLs could represent customer locations where internet or phone services are provided. SLs are the starting point of mapping because they mark the end destination for resources, whether it’s electricity, data, or other services. Identifying these locations is crucial for ensuring that the correct amount of power or data is distributed efficiently and monitored effectively.
Physical Nodes (PNodes):
Physical Nodes, often referred to as PNodes, are critical parts of any infrastructure network. They are physical points in a system where energy, data, or other services are transmitted or received. In an electrical grid, PNodes are the locations where electricity is either generated or distributed, and they link service locations to the overall network. Similarly, in telecommunications, PNodes might refer to routers, switches, or servers that control the flow of data. Mapping SLs to PNodes helps track the connection between where services originate and where they are delivered, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
Zones:
Zones in the SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. represent groups of SLs and PNodes that are organized together for better control and management. Zones help simplify the complex mapping of nodes and service locations by breaking the system into manageable parts. For example, a city might be divided into several zones based on the locations of different power stations or network hubs. Grouping SLs and PNodes into zones makes it easier for operators to monitor, troubleshoot, and balance loads between different areas. Zones also help with strategic planning, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently across different regions.
How Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping Works
Step-By-Step Explanation Of Mapping Sls To Pnodes And Allocating Them Into Zones:
The process of SL to PNode to Zone Mapping is fairly straightforward but essential for efficient management of networks and resources. Here’s how it works:
- Identify Service Locations (SLs):
First, you begin by listing all the Service Locations (SLs). These are the end points where services like electricity or data are delivered. Every SL is marked with its unique identifier and location. - Map SLs to PNodes:
Once the SLs are identified, the next step is to connect them to the corresponding Physical Nodes (PNodes). PNodes are points where electricity or data enters or exits the network. This mapping ensures that each SL is linked to the correct PNode, which controls the flow of resources to that specific location. This step is vital for monitoring the transmission of energy or data and ensuring everything is working properly. - Allocate Zones:
After SLs are mapped to PNodes, the system is then divided into Zones. Zones are larger areas that group together multiple PNodes and SLs for easier control and management. Organizing PNodes and SLs into zones helps simplify operations, especially for large grids or networks. This makes it much easier to monitor and manage multiple service points efficiently.
Importance of This Mapping for Managing Network Infrastructure and Energy Grids:
Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping Is Crucial For Several Reasons:
- Real-Time Monitoring: By mapping out SLs, PNodes, and Zones, operators can monitor the flow of electricity or data in real time. This means that any disruptions, inefficiencies, or outages can be quickly identified and fixed. Without this clear mapping, identifying the source of a problem would be much harder.
- Efficient Load Balancing: Networks and grids must balance loads to avoid overloading any single PNode or zone. This mapping allows managers to understand where the demand is highest and adjust the distribution accordingly. Load balancing helps prevent outages and maintains stable service across all regions.
- Planning and Expansion: This mapping is not only useful for managing current operations but also helps with future planning. By having a clear understanding of the relationships between SLs, PNodes, and Zones, companies can forecast future needs, plan expansions, and avoid potential bottlenecks in service delivery.
Examples Of How This Mapping Optimizes Network Performance:
- Electricity Distribution: In the energy sector, utilities use SL to PNode to Zone Mapping to optimize the flow of electricity across their grids. By clearly mapping service points to power nodes, companies ensure that no part of the grid is overloaded and that electricity is distributed evenly. For instance, during peak hours, operators can adjust the distribution of power across different zones to avoid overloading any single area.
- Load Balancing in Data Networks: In telecommunications, mapping SLs to PNodes and Zones ensures that data is transmitted efficiently across networks. This mapping helps balance traffic across different servers and routers, preventing any one part of the network from becoming overwhelmed by high demand.
- Emergency Response: When there’s an outage or failure in a network or grid, SL to PNode to Zone Mapping makes it easier to locate the problem and deploy emergency fixes. Operators can quickly see which SLs and PNodes are affected and take action to resolve the issue in the affected zone first, ensuring critical services like hospitals or emergency responders get priority restoration.
Benefits Of Using Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping.xlsx.
Efficiency And Accuracy:
One of the biggest advantages of using SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. is its ability to improve both efficiency and accuracy. The structured format of the Excel sheet ensures that data entry follows a systematic approach, reducing the likelihood of errors. Each Service Location (SL), Physical Node (PNode), and Zone are entered methodically, making it easier to track and monitor how data or resources are distributed. When data is organized in a clear, structured way, it’s much easier to analyze and maintain accuracy over time. This is particularly important in industries like energy management and telecommunications, where mistakes in data mapping could lead to costly errors.
Versatility:
Another major benefit of this Excel tool is its versatility. SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. can be used across a range of industries including energy, logistics, telecommunications, and even large-scale retail operations. Its basic structure of mapping service points, nodes, and zones applies to any system that requires resource distribution, whether that’s electricity, data, or even physical goods. This flexibility makes it an essential tool for various organizations looking to optimize their operations. From tracking power flow in an electrical grid to managing delivery routes in logistics, the tool adapts easily to different industries.
Data Organization And Scalability:
As businesses grow, the amount of data they need to handle increases. SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. is designed to handle both small-scale and large-scale projects efficiently. The tool’s scalability allows organizations to manage larger datasets without losing control over accuracy or performance. Whether you’re managing a few service locations or a large network of thousands, the tool’s structured layout helps organize data in a way that’s easy to expand as your project grows. For example, energy companies can add new zones and PNodes as they expand their grid, and logistics companies can use the same structure to manage additional delivery routes or service areas.
Common Challenges In Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping
Data Entry Errors:
One common challenge when working with SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. is data entry errors. Even a small mistake, like entering the wrong location or node, can result in inaccurate mappings. These errors may lead to incorrect resource allocation, disruptions in service, or financial losses. To avoid this, it’s crucial to double-check data inputs and apply validation rules within the Excel sheet. Automated checks can help catch mistakes early, but manual reviews are also important for ensuring accuracy.
Mapping And Performance Issues:
As datasets grow larger, mapping errors and performance issues can arise. Large Excel files may start to slow down, making it difficult to process information quickly. In some cases, the file may even become too slow to work with efficiently. This is especially a problem when managing large grids or networks with thousands of data points. To optimize performance, users can break down large datasets into smaller, more manageable files or use advanced Excel features like pivot tables and formulas that reduce unnecessary calculations. Optimizing the file structure can also help avoid performance lags.
File Corruption And Lack Of Training:
Another issue users may face is file corruption. Excel files, particularly those that are large and frequently updated, are prone to corruption. This can lead to loss of important data and functionality. Regular backups are essential to prevent data loss, and Excel’s built-in recovery tools can sometimes repair corrupted files. In addition to file corruption, a lack of training can make the tool difficult to use effectively. Without proper knowledge of Excel functions and mapping techniques, users may struggle with errors or inefficiencies. Offering training and creating user-friendly guides can help ensure smooth operation and prevent avoidable mistakes.
Best Practices For Managing Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping
Regular Updates And Data Validation:
To keep the SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. accurate and reliable, it’s crucial to perform regular updates and data validation. Data in the Excel sheet must reflect current conditions, such as new service locations (SLs), changed PNodes, or updated zone boundaries. This prevents outdated information from leading to incorrect resource allocation or service disruptions. Implementing periodic reviews of the mapping file helps ensure data integrity. For better accuracy, Excel’s data validation tools can prevent incorrect entries by restricting the types of data allowed in specific cells. This helps users catch errors at the time of entry, reducing future troubleshooting.
Automation Tools:
Excel provides powerful automation tools that can save time and reduce human errors in managing large datasets. Features like conditional formatting can highlight important data points, making it easier to identify issues, such as overloading in certain zones or discrepancies between SLs and PNodes. Pivot tables help summarize complex data, allowing for quick analysis of relationships between service locations, nodes, and zones. Moreover, macros automate repetitive tasks, such as data entry or validation, and reduce manual errors. These tools enhance efficiency and make the mapping process much smoother, especially when handling large-scale projects.
Backup And Documentation:
Given the complexity and importance of the data stored in the SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx, it’s critical to back up the file regularly. File corruption or accidental deletion can cause significant losses, so having a backup system ensures you can recover data quickly if needed. Along with backups, maintaining version control is essential. Keeping track of changes allows you to revert to previous versions if errors occur during updates or modifications. Additionally, documenting these changes ensures that team members understand the modifications and can work consistently, minimizing confusion when the file is passed between departments or team members.
Case Studies And Real-World Applications
Energy Sector Success Stories:
In the energy industry, companies have used SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. to improve their resource management and grid performance. For example, a major utility provider used the mapping file to optimize electricity distribution across different zones. By accurately mapping service locations to PNodes, they achieved better load balancing, reduced power outages, and improved overall grid reliability. This helped the company cut down on maintenance costs and deliver more consistent service to customers.
Telecommunications Industry Applications:
Telecom companies frequently rely on SL to PNode to Zone Mapping to track data flow and manage network resources. One large telecom firm implemented this tool to monitor data transmission between service locations and network nodes, leading to more efficient handling of bandwidth and faster issue detection. By using the mapping file, they optimized their network, which resulted in improved customer satisfaction through faster internet speeds and fewer network disruptions.
Logistics Sector Use Cases:
In logistics, companies have used SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. to improve delivery route efficiency. For instance, a logistics company mapped its distribution centers to delivery nodes and zones to create more efficient delivery schedules. By grouping service locations into optimized zones, the company was able to reduce fuel costs, shorten delivery times, and boost customer satisfaction. The mapping tool allowed them to analyze and reorganize routes based on changing demand patterns, improving overall operational efficiency.
Improvements In Operational Efficiency And Cost Savings:
Across different industries, the use of SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. has led to significant improvements in operational efficiency. By organizing service locations, physical nodes, and zones in a clear and structured way, businesses can make better decisions regarding resource allocation and planning. This results in cost savings, fewer service disruptions, and increased performance. In all cases, accurate mapping contributes to more effective management, whether it’s electricity, data, or logistics operations, ensuring that companies can scale their services while maintaining efficiency.
Comparison With Other Mapping Tools
When comparing SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. with other specialized mapping tools, like Geographic Information Systems (GIS), there are clear distinctions in usability and functionality.
GIS software is highly advanced and designed for complex spatial data analysis. It offers powerful tools for visualizing geographical data, performing spatial analysis, and generating maps. GIS tools can handle massive datasets and provide real-time analytics, making them ideal for projects that require in-depth geographic mapping, such as city planning or large-scale infrastructure management. However, they often require extensive training, are costly, and may involve significant resource investments to implement.
On the other hand, SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. is much simpler to use and is highly customizable. It leverages the familiarity of Excel, making it accessible for individuals and businesses that don’t need the complexity of GIS. While it lacks some of the advanced features of specialized mapping tools, Excel-based mapping allows users to organize data, automate processes with macros or pivot tables, and tailor the tool to specific needs without the high cost or technical expertise required by GIS. This makes Excel a preferred solution for smaller businesses or less complex projects, where flexibility and simplicity are valued over advanced spatial analysis.
Future Trends In Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping
The future of SL to PNode to Zone Mapping is poised to evolve with the integration of technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). These innovations will allow for more efficient data mapping by automating complex tasks and detecting patterns in data that might otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, AI can help in predicting energy consumption trends, optimizing grid performance, or even suggesting adjustments to load balancing in real-time.
Machine Learning algorithms can continuously analyze data from SLs and PNodes, providing more accurate forecasts and enabling automated adjustments to network configurations, leading to a more responsive and efficient grid or network system. Moreover, real-time data mapping is expected to become a norm, where systems can automatically update the mapping as new SLs, PNodes, or zones are added or changed. This will make SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. not only a tool for static mapping but also a dynamic system that adapts as data flows in real time.
Looking ahead, advanced data analytics tools integrated with mapping processes will give organizations better insights into performance and future demands, enhancing both short-term operations and long-term planning.
Conclusion
In summary, SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx. plays an essential role across multiple industries, from energy and telecommunications to logistics. Its simplicity, versatility, and customizability make it a highly effective tool for managing complex data related to service locations, physical nodes, and zones. Whether used for optimizing resource distribution or improving operational efficiency, this mapping tool has proven its value in a variety of real-world applications.
The key to maximizing the benefits of SL to PNode to Zone Mapping lies in maintaining data accuracy, performing regular updates, and utilizing the right tools for automation and analysis. As industries continue to grow and technologies like AI and ML become more integrated, this tool will remain an essential part of managing networks and ensuring efficient resource allocation in an increasingly data-driven world.
FAQ:
What Is Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping.xlsx Used For?
SL to PNode to Zone Mapping.xlsx is primarily used to map Service Locations (SLs) to Physical Nodes (PNodes) and organize them into zones for better management. It helps industries like energy, telecommunications, and logistics optimize resource distribution and network performance.
How Does This Tool Help In Energy Management?
In energy management, this tool helps map the flow of electricity from power nodes to service locations. It allows operators to monitor electricity distribution, balance loads, and address issues like power outages efficiently.
Can Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping.xlsx Be Customized For Different Industries?
Yes, the Excel-based format is highly customizable. It can be adapted for various industries, such as energy grids, telecom networks, or logistics operations, by modifying the columns and data entry fields according to the specific needs of the project.
What Are The Common Challenges With Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping?
Common challenges include data entry errors, file corruption, and performance issues when handling large datasets. Regular updates, data validation, and backups are crucial to maintaining accuracy and avoiding these problems.
How Does Automation Improve The Efficiency Of This Tool?
Using Excel’s built-in features like macros, conditional formatting, and pivot tables can automate repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and make data analysis quicker and more efficient. This helps manage large-scale projects more effectively.
What Are Future Trends For Sl To Pnode To Zone Mapping?
Future trends include the integration of AI and machine learning to enhance data mapping accuracy, real-time updates, and advanced analytics for better forecasting and resource optimization. These innovations will automate many aspects of the mapping process.
Thank you for exploring our Blog! For additional captivating content, feel free to explore the corresponding category.
Understanding The Kysely Date_Trunc Is Not Unique Issue: Causes, Solutions, And Best Practices